In today’s digital age, accessing the internet has become an essential part of our daily lives. Whether it’s for work, education, entertainment, or communication, the internet plays a crucial role. But have you ever wondered how you’re able to connect to the internet? This is where an ISP, or Internet Service Provider, comes into play. In this article, we’ll delve into what an ISP is, how it works, the different types available, and why it’s important to choose the right one for your needs.
What is an Internet Service Provider (ISP)?
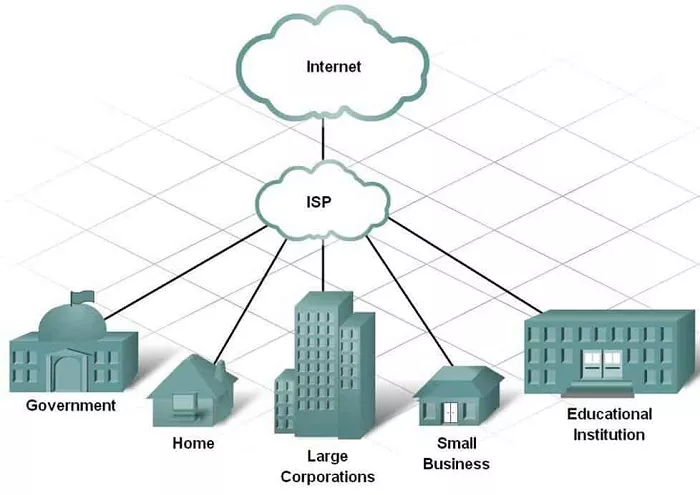
An Internet Service Provider (ISP) is a company or organization that offers services for accessing, using, or participating in the internet. ISPs provide the infrastructure and services that allow individuals and businesses to connect to the internet. They offer various types of internet connections, such as dial-up, DSL, cable, fiber-optic, and satellite.
ISPs not only provide internet access but may also offer additional services like email accounts, web hosting, domain registration, and customer support. They play a vital role in ensuring that users can browse websites, stream videos, send emails, and perform other online activities seamlessly.
How Does an ISP Work?
Understanding how an ISP functions can help you appreciate the complexity behind your internet connection. Here’s a simplified explanation:
- Infrastructure Setup: ISPs establish a network infrastructure that includes servers, routers, and data centers. This infrastructure connects to the broader internet backbone, which is a global network of high-capacity data routes.
- Connection to Users: ISPs connect users to their network through various means, such as telephone lines, coaxial cables, fiber-optic lines, or satellite signals. The type of connection depends on the technology the ISP uses and the user’s location.
- IP Address Assignment: When you connect to the internet through an ISP, you’re assigned an IP (Internet Protocol) address. This unique identifier allows your device to send and receive data over the internet.
- Data Transmission: ISPs manage the flow of data between your device and the internet. They ensure that data packets are transmitted efficiently, allowing you to access websites, stream content, and use online services.
- Additional Services: Many ISPs offer supplementary services, such as email hosting, security features, and customer support, to enhance the user experience.
Types of Internet Connections Offered by ISPs
ISPs provide various types of internet connections, each with its own characteristics, advantages, and limitations. Here’s an overview of the most common types:
1. Dial-Up
- Description: One of the earliest forms of internet connection, dial-up uses telephone lines to connect to the internet.
- Speed: Typically up to 56 Kbps.
- Pros: Widely available in areas with telephone lines.
- Cons: Extremely slow speeds and inability to use the phone line for calls while connected.
2. DSL (Digital Subscriber Line)
- Description: DSL also uses telephone lines but offers higher speeds than dial-up.
- Speed: Ranges from 256 Kbps to over 100 Mbps, depending on the service.
- Pros: Allows simultaneous use of the internet and telephone; widely available.
- Cons: Speed can decrease with distance from the ISP’s central office.
3. Cable
- Description: Utilizes coaxial cables, the same used for cable television, to provide internet access.
- Speed: Typically ranges from 10 Mbps to 1 Gbps.
- Pros: Faster speeds compared to DSL; widely available in urban areas.
- Cons: Bandwidth is shared among users in the area, which can lead to slower speeds during peak times.
4. Fiber-Optic
- Description: Uses thin strands of glass or plastic fibers to transmit data as light signals.
- Speed: Can exceed 1 Gbps.
- Pros: Extremely high speeds and reliability; ideal for heavy internet usage.
- Cons: Limited availability; higher installation costs.
5. Satellite
- Description: Provides internet access via communication satellites.
- Speed: Typically ranges from 12 Mbps to 100 Mbps.
- Pros: Available in remote or rural areas where other connections are not feasible.
- Cons: Higher latency; affected by weather conditions; data caps may apply.
6. Wireless (Fixed Wireless and Mobile Broadband)
- Description: Delivers internet access through radio signals from a local tower to a receiver at the user’s location.
- Speed: Varies widely based on technology and location.
- Pros: Quick installation; suitable for areas without wired infrastructure.
- Cons: Signal strength can be affected by obstacles and distance from the tower.
Services Provided by ISPs
Beyond just internet access, ISPs often offer a range of additional services to cater to the diverse needs of their customers:
- Email Services: Many ISPs provide email accounts with storage and spam filtering.
- Web Hosting: Hosting services for personal or business websites.
- Domain Registration: Assistance in registering and managing domain names.
- Security Features: Tools like firewalls, antivirus software, and parental controls.
- Technical Support: Customer service to help with connectivity issues and other concerns.
- Bundled Services: Packages that include internet, television, and phone services.
Choosing the Right ISP
Selecting an ISP involves considering several factors to ensure it meets your specific needs:
- Availability: Not all ISPs operate in every area. Check which providers are available in your location.
- Speed Requirements: Determine the internet speed you need based on your activities. Streaming, gaming, and large downloads require higher speeds.
- Cost: Compare pricing plans, including installation fees, equipment rentals, and monthly charges.
- Data Caps: Some ISPs impose limits on data usage. Be aware of these caps to avoid additional charges.
- Reliability: Research the ISP’s reputation for uptime and consistent service.
- Customer Support: Consider the quality and availability of customer service.
- Contract Terms: Review the length of contracts, cancellation policies, and any promotional rates.
The Role of ISPs in Internet Privacy
ISPs play a significant role in internet privacy, as they can monitor and log user activity. This has raised concerns about data security and privacy. To mitigate these concerns:
- Use of VPNs: A Virtual Private Network (VPN) encrypts your internet traffic, making it difficult for ISPs to track your online activities.
- HTTPS Websites: Accessing websites that use HTTPS ensures that data transmitted between your browser and the website is encrypted.
- Privacy Policies: Review your ISP’s privacy policy to understand how your data is handled.
Conclusion
Internet Service Providers are the backbone of our online experiences, enabling us to connect, communicate, and access a wealth of information. Understanding what ISPs are, how they operate, and the services they offer empowers you to make informed decisions about your internet needs. By considering factors like connection types, additional services, and privacy implications, you can choose an ISP that aligns with your requirements and ensures a reliable and secure internet experience.