In today’s digital age, staying connected to the internet is essential for work, education, entertainment, and communication. Behind every internet connection is an Internet Service Provider (ISP), the company that enables access to the vast online world. This article provides a comprehensive yet straightforward explanation of what ISPs are, how they function, the types available, and how to choose the right one for your needs.
What Is an Internet Service Provider (ISP)?
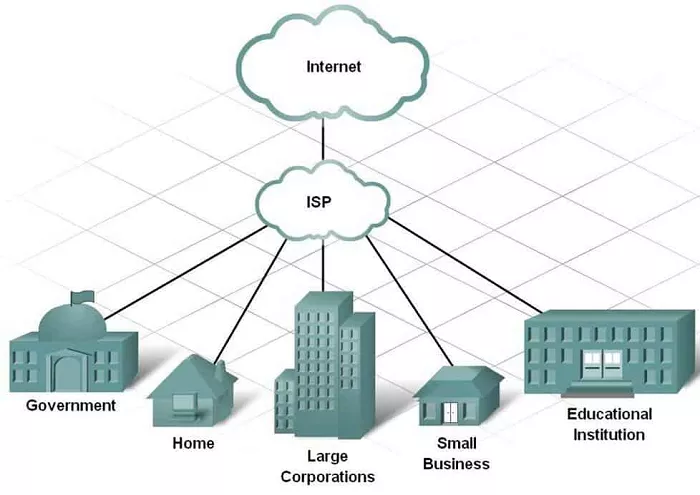
An Internet Service Provider (ISP) is a company that offers individuals and organizations access to the internet. ISPs use various technologies to connect users to the internet, including cable, DSL, fiber-optic, satellite, and wireless connections. Beyond internet access, many ISPs also provide additional services such as email accounts, web hosting, and domain registration.
How Do ISPs Work?
ISPs operate by maintaining the infrastructure necessary to provide internet connectivity. They own or lease physical networks, including cables, servers, and routers, which facilitate data transmission between users and the broader internet. ISPs connect to larger networks or internet backbones, allowing data to travel across the globe. When you access a website or send an email, your data travels through your ISP’s network to reach its destination.
Types of ISPs
ISPs can be categorized based on their size, infrastructure, and the services they offer. Understanding these types can help you choose the right provider.
Tier 1 ISPs
Tier 1 ISPs are large companies that own extensive networks and have direct access to the entire internet without paying other providers. They form the backbone of the internet, connecting with other Tier 1 ISPs to exchange data freely. Examples include AT&T and Verizon.
Tier 2 ISPs
Tier 2 ISPs purchase internet access from Tier 1 providers and may also connect with other Tier 2 ISPs. They often serve regional or national markets, offering services to consumers and businesses.
Tier 3 ISPs
Tier 3 ISPs are local providers that purchase internet access from Tier 2 or Tier 1 ISPs. They focus on delivering internet services to end-users, such as homes and small businesses.
Types of Internet Connections Offered by ISPs
ISPs offer various types of internet connections, each with its advantages and limitations.
Dial-Up
An older technology that uses telephone lines to connect to the internet. It offers very slow speeds and is largely obsolete today.
DSL (Digital Subscriber Line)
Utilizes existing telephone lines to provide internet access. DSL offers moderate speeds and is widely available, especially in areas without cable infrastructure.
Cable
Uses coaxial cable lines to deliver internet service. Cable internet offers higher speeds than DSL and is common in urban and suburban areas.
Fiber-Optic
Employs thin strands of glass or plastic fibers to transmit data as light signals. Fiber-optic internet provides extremely high speeds and reliability but may have limited availability.
Satellite
Connects users to the internet via satellites orbiting the Earth. Satellite internet is useful in remote areas but can have higher latency and lower speeds.
Wireless (Fixed Wireless and Mobile Broadband)
Delivers internet service through radio signals from a wireless tower to a receiver at the user’s location. It’s beneficial in areas lacking wired infrastructure.
Services Provided by ISPs
Beyond internet access, ISPs may offer a range of additional services:
- Email Accounts: Providing users with email addresses and related services.
- Web Hosting: Hosting websites on their servers.
- Domain Registration: Allowing users to register and manage domain names.
- Virtual Private Network (VPN) Services: Offering secure connections for privacy and security.
- Technical Support: Assisting customers with connectivity issues and other technical problems.
Choosing the Right ISP
When selecting an ISP, consider the following factors:
1. Availability
Not all ISPs are available in every area. Check which providers operate in your location.
2. Speed
Determine the internet speed you need based on your activities, such as streaming, gaming, or remote work.
3. Cost
Compare pricing plans, including installation fees, equipment rental, and monthly charges.
4. Reliability
Research the ISP’s reputation for consistent service and minimal downtime.
5. Customer Service
Consider the quality of customer support, including availability and responsiveness.
The Role of ISPs in Internet Access
ISPs play a crucial role in connecting users to the internet, enabling access to information, communication, and services worldwide. They invest in infrastructure, maintain networks, and ensure data can travel efficiently across the globe. As technology evolves, ISPs continue to adapt, offering faster speeds and more reliable connections to meet growing demands.
Conclusion
Understanding what an ISP is and the services they provide is essential in today’s connected world. By offering various types of internet connections and additional services, ISPs cater to diverse needs, from individual users to large organizations. When choosing an ISP, consider factors like availability, speed, cost, reliability, and customer service to find the best fit for your requirements.